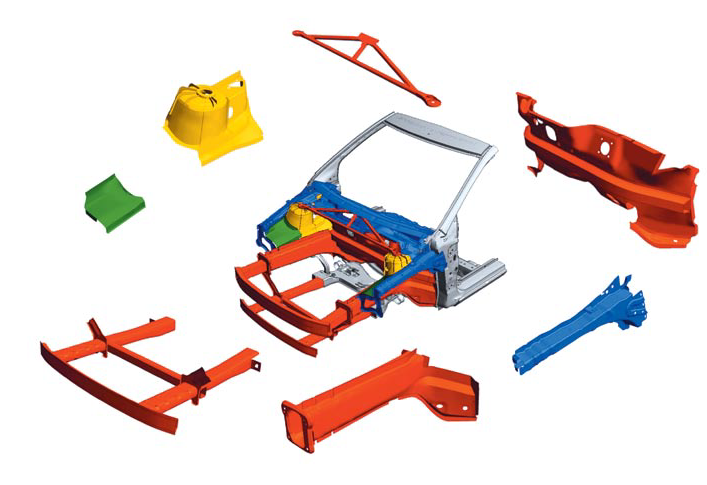
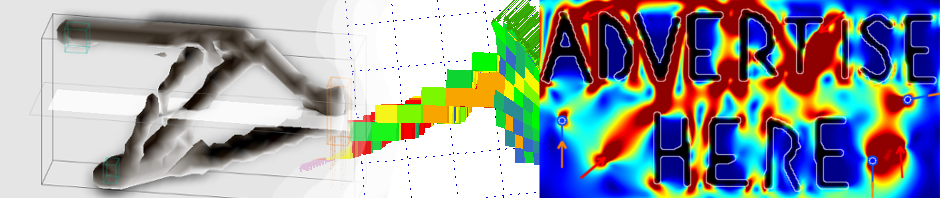
This nice presentation (link) shows us the wonderful BIW of BMW 5 GT. This is the first family car BIW that I have seen that has so many indications of being topology optimized. Just look at the following picture to see what I mean: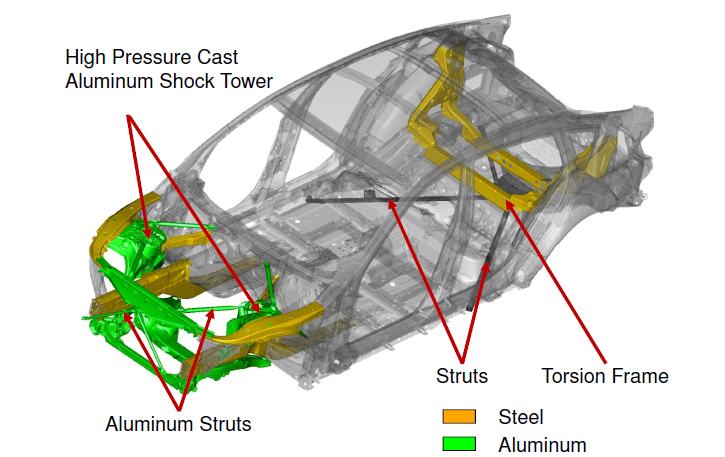
The fron section with all those struts and interestingly shaped structures is evidently the most direct application of big scale topology optimization in any family car. As a result it has a very high torsional rigidity of 31500 Nm/° higher than some supercar’s rigidity. Also the variety of materials used in the body is interesting. 14 types of steel and 7 types of aluminum alloys are used, seemingly utilizing the most suited material in wherever needed. The BIW is mostly steel with aluminum body panels.